Search
User login
Topic “Secondary (11-16yrs)”
Secondary school age (11-16 years)
Auditory discrimination of minimal pairs
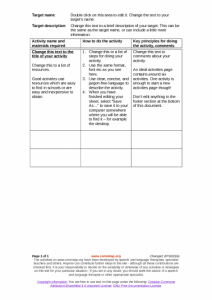
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Main instructions Pictures of minimal pair words (e.g. key/tea) - photocopy them on to card (e.g. 6 of each word) so that you can't see through the card. | 1. Put one of each picture (e.g. key and tea) on the table, face up. 2. Mix up the rest of the pictures and put them in a pile face down. 3. Take one picture from the pile, don't let the person see it! 4. Say what is on the picture (e.g. key). 5. Make sure you present the pictures in a random order so that the person can't predict what's coming next. 6. The person has to find the appropriate picture on the table. | These are the main instructions for the activities. Use this with the games below. |
| Lotto game Lotto boards (4 pictures to a board. Use pairs of words from the list above, but do not put both words of a pair on the same board) Corresponding picture cards |
Make a choice at snack time
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Snack activity Food items - in small pieces - which the children like, for example banana, apple, orange, crisps; Something uninteresting - e.g. a piece of paper; Pictures of the food items. |
| Key strategies - you may need to come back to these as and when necessary: Introduce each food item; Check which ones the child is interested in; Demonstrate the asking for and getting of an item - e.g. with another member of staff; Wait - give time for the child to respond or initiate; Offer a "forced alternative", e.g. "apple or orange?" - swap around the order in which you give the alternatives to check that the child is not just saying the last thing you say; Make it difficult for the child to communicate by pointing by having the choices close together and out of reach - so if they point you actually don't know which one they pointed to; Be sensitive to if the child is getting frustrated - think of ways to help them get it right first time - e.g. by reducing the choice down to one item (temporarily). Using forced alternatives: Always give the child the thing they said/signed for. If they are having difficulties with this - for example always say the last thing in the alternative, try the following: Have one of the forced alternatives being something uninteresting (e.g. the piece of paper); Have the last alternative as something the child doesn't want (if the child always says the last thing); Give more emphasis to the desired item, e.g. "Banana or paper?", you could also try only signing the desired item. Over time, reduce the difference in emphasis. Improving clarity Sometimes the child may say/sign what they want, but you don't feel it is clear enough (perhaps you can understand it in this context but might not be able to in another situation). To try and improve this, you can try: Saying 'pardon?' or something equivalent; Look confused and say, for example '(Do you mean) apple or banana?' (saying and signing these) - this will often encourage the child to produce a clearer version; Simply re-inforce with the clear version, e.g. you say "Oh, banana" (saying and signing it then passing it over); Try to avoid simply asking the child to repeat after you as there is no communication and it's not a natural way to communicate - by asking the child to repeat you have shown them that you have understood, and so this is now a different repetition activity - it also has the danger that it could reduce the accuracy of what the child originally said or signed as they didn't get a direct result from this.
|
Request a desired item
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Snack time
|
See the comments on the right as to how to respond to some typical situations. | What to do in common scenarios The person points at or tries to take the item. Hold or place the items in such a way that they can't easily take them and so that even if they point it is not clear which one they are choosing (once you know - and the person knows you know - which one they want simply now asking them to repeat what you had hoped they would have requested is much less powerful for learning). The person always asks for the last thing you said (e.g. always asking for a crisp): Try reversing the order of the choice you give them; If they don't seem to care which one you give them, give them a choice of a desirable item and a boring item - saying the boring item last - then respond to their request for the boring item. To stop frustration, you might need to quickly follow this up with another go where you only offer them one item (the desirable item); Encourage them to point to a picture to show you which one they want - then reinforce this by signing and saying the word. General strategies Model the asking and requesting with someone (e.g. other staff) to show what you are hoping people to do. |
To use language to describe the characteristics and functions of objects
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| What's in the bag? - Bag - A selection of objects or pictures - click below for printable object pictures: - Question prompt cards - click here to print.
| 1. Explain to your child/student that you are all going to take it in turns to put something in the bag and describe it for others to guess. 2.Model the game for the first turn. Give a description of your obejct for the others to guess. 3. Swap and let your child/student have a turn. If your child/student is finding it hard to think of things to saym you can use the questions cards to help support them. | |
| Treasure Hunt - Objects to hide around the room (optional) | ||
| Taboo! . |
Key Word Signing
Key word signing is used with people with communication and/or learning difficulties. Key word signing is always done whilst speaking, and you use it to sign the most important words that you are saying at an appropriate level for the person you are signing with.
Aware of changes in daily routine
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Usual timetable Picture symbols which represent each activity in the day (and/or use words if the child understands these) with velcro on the back; Velcro board to stick them to; A normal day! You can find picture symbols with the Commtap Symboliser. |
| This activity is about ensuring that the child understands their usual timetable. Do this activity on a 'normal' day (or at least one that is likely to be normal). The child should be able to understand the pictures or words you use for the timetable. If not, you should spend some time showing the child the picture symbol word when they are doing the activities in the routine. See also: "Use a visual timetable" on the Commtap site. If a whole day is too much, you could do this over a part of the day - for example the morning or the afternoon. |
| Timetable - day which is different Picture symbols which represent each activity in the day (and/or use words if the child understands these) with velcro on the back; Velcro board to stick them to; A day which is different. You can find picture symbols with the Commtap Symboliser. | Ideally, the child should already be able to construct the timetable for the 'normal' day with minimal prompting. |
Activities Sheet Template
This is a Word template which can be used to make an activities sheet in the standard format used on the Commtap site.
Created 7 October 2011; updated 16 July 2015.
Commtap Logo
Picture:

Picture description:
The Commtap logo.
Develop language skills through cookery
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Deciding on the ingredients Pen; Paper; Optional - picture symbols for food items you need; An idea for what you are going to make. If using, you can make picture symbol cards using the Commtap Symboliser for PowerPoint. |
See comments for variations on doing this. | Making it easier: Have a set of pictures of ingredients which are appropriate for what you are making, and some other ingredients. Get the children to choose the appropriate ingredients. Even easier: Have a set of pictures for the ingredients, and some further pictures which aren't food (e.g. pictures of furniture, clothes). Help the child to choose those which are food items. Harder: Get the children to draw and/or write down the ingredients themselves. |
| Buying ingredients
You can make a shopping list with symbols using the Commtap Symboliser for PowerPoint. | On subsequent occasions, you can pretend that you have a really bad memory, and you need the children to help you to remember what to take. If they don't remember everything, you can look a bit confused, and say something like "I'm sure we need to take something else...". You could also use ideas based on the comments in "Deciding on the ingredients". | |
| Making the item
| If the children are familiar with cooking this item, but they sequenced the pictures for doing the activity incorrectly at the beginning, you don't necessarily have to correct them straight away - you can correct it at the point when it becomes a problem - e.g. if you get to the putting the pizza in the oven bit before you've put the sauce and toppings on (look very confused!). Sketches for the sequence - these do not need to be accurate at all - they will be useful for this activity no matter what level of drawing ability you have. The children can also help with this. You can incorporate a number of maths concepts into the activities, for example: "full", "empty", "more", "less", "hot", "cold". Safety. Clearly you will need to manage any dangerous aspects of the cooking process as appropriate for the children you are working with (e.g. use of knives, the cooker). |
Nose
Picture:

Picture description:
Nose graphic.
Letter set (i h j k)
Picture:
Picture description:
Set of four letters (i, h, j, k).
Part of a letter rainbow
Picture:
Picture description:
First few letters of a letter rainbow.
Letter rainbow
Picture:
Picture description:
Letter rainbow.
because sentence frame
Picture:
Picture description:
Three part sentence frame example linking phrases with because.
Support Commtap to keep it online
Thank you for visiting Commtap.
Please read this message as it is extremely important.
- Visitor donations mean we can continue to host over 1,000 free activities to support speech, language, and communication development.
- Visitor donations mean we can continue to provide free resources to address a wide range of communication needs, including limited speech or language, interaction challenges, and needs associated with conditions such as developmental language disorder, autism, and cerebral palsy.
- Visitor donations mean we can continue to provide resources to support the work of speech and language therapists, teachers, teaching assistants, parents, and carers.
- Visitor donations mean we can continue to provide the free key word sign dictionary (bks.org.uk) which has over 2,000 Makaton and Signalong signs.
We know that not everyone is able to afford to pay to access these resources, however, if you can, please make a donation to keep the site going.
Thank you
Google ads on this page are provided by Google Adsense - and their presence does not imply any endorsement by Commtap. Report a problem with an ad on this page. Log in (for free) to avoid seeing Google ads.