Search
User login
Topic “Primary (5-11yrs)”
Primary school age (5-11 years)
How are you conversation prompt pictures
Picture:
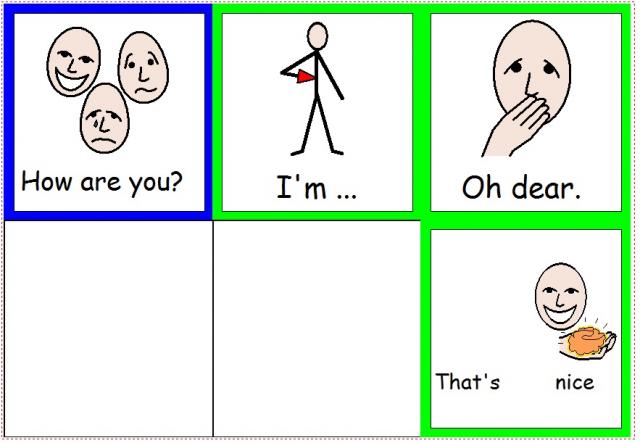
Picture description:
Prompt pictures for three turns in a conversation beginning "How are you?"
List of common synonyms
Some common synonyms:
| Woman | Lady |
| Road | Street |
| Rug | Mat |
| Flower | Bloom |
The Chute
The chute is a special/fun posting box which is designed for posting cards with something on each side. You post it with one side facing up, and it pops out of the bottom showing the other side. You could use this for phonology work for example, having picture cards with the initial sound written on the back. The pupil says the initial sound for the picture, posts the card and checks if they were right from the card when it comes out the bottom.
How to make the chute
You will need:
The Chute
Picture:

Picture description:
The chute - a special kind of posting box.
Diagram of the Chute
Picture:

Picture description:
Diagram of the chute - a special kind of posting box.
Simple topic maintenance
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| My interests |
| |
| Topic introduction
| ||
| Talk about it
| Optional:
| |
| Likes and dislikes Something to record the students responses on (e.g. paper/pen) which can later be used as a prompt; Soft ball or beanbag. | To make it harder, you can go around again asking for favourite drinks - so that everyone now has to remember a food and a drink for each student when they pass the ball (e.g "Tim - (you like) carrot cake and tea"). You could use favourite games, favourite places to go, etc. instead. | |
| What have you done today? Way of recording students responses - e.g. paper/pen, whiteboard/marker; Soft ball or beanbag. |
Strategies for eliciting single words/short phrases/gestures
| Activity name/materials | Instructions | Comments |
| Wrong picture names! Materials: Set of pictures of everyday objects - these should be cards that the child knows the names of |
Strategies for eliciting single words/short phrases/gestures
Created 3 October 2014; updated 27 August 2015.
Select a picture on an eye gaze frame
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Picture pairs Plastic perspex sheet with hole in the middle, around 40cm x 30cm (e.g "E-tran frame"); Two sets of everyday picture cards - or whatever the student is interested in. |
| If the student has difficulties, you can try pointing it at each position on the frame - starting from their top left and working across and down - say "is it here" at each position ("no!") - until you get to the right position, say "yes" "here's the....". Say "look at the....", then ask them and say "where was the....?" - taking your eyes slowly to the position - trying to take the student's eyes with you. When you get there, take it off, pretend to eat it (for example) and then put it on the "done" pile with the other card. More ideas about this here from Call Scotland. Going further When a student can do this with one picture, try adding more pictures on the frame (distractor pictures). Start with two, then three/four (one on each corner), then gradually up to seven (each corner and the middle of each side except the bottom side. Put the target card - the one you are working on - in one of the positions you are using. |
| Find the picture/item Plastic perspex sheet with hole in the middle, around 40cm x 30cm (e.g "E-tran frame"); Two sets of everyday picture cards - or whatever the student is interested in. | If the student has difficulties, you can try pointing it at each position on the frame - starting from their top left and working across and down - say "is it here" at each position ("no!") - until you get to the right position, say "yes" "here's the....". Say "look at the....", then ask them and say "where was the....?" - taking your eyes slowly to the position - trying to take the student's eyes with you. When you get there, take it off, and pretend to eat it/drive it etc. More ideas about this here from Call Scotland. Going further When a student can do this with one picture, try adding more pictures on the frame (distractor pictures). Start with two, then three/four (one on each corner), working up to seven (each corner and the middle of each side except the bottom side. Put the target card - the one you are working on - in one of the positions you are using. | |
| Confirmation using a "special spot" Plastic perspex sheet with hole in the middle, around 40cm x 30cm (e.g "E-tran frame"); Two sets of everyday picture cards - or whatever the student is interested in. | The idea of this activity is for the student to learn how they can confirm a choice. It is necessary to have some way of them confirming a choice because:
All these will make it difficult to be sure what they are trying to communicate. The "special spot" (which could for example be a red circle stuck in the bottom middle of the frame) can be a point that a student to look to to:
|
Responds to who what and why
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| The who/what/why sheet Sheet with 3 columns, one headed "who?", one headed "what?", one headed "why?" Brick cube 'Wh' word symbols You can make these resources using the Commtap Symboliser for PowerPoint. |
|
Responds to why questions
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Emotions picture cards Picture cards with emotions Optional - choice of pictures showing possible reasons - for example a picture of a boy who has fallen over to go with a picture of a boy who is crying. |
| |
| Why is it.... One or more pictures showing scenes - for example someone running away, a hot beach. Or... Pictures in a book. | ||
| A desirable and a non-desirable toy Two toys one desirable and one not. |
Responds to what questions
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Familiar picture books
|
| WARNING: it can become a habit to keep asking a child "what's that" whenever you see a picture (a phenomenom that might be called "What's that-ing") - so use in moderation - and, in other situations, try leaving long pauses for a child to tell you about a picture rather than asking a specific question. When the child is able to understand this question, you could try taking it in turns so that they get a go at asking you "what's that?". |
| Silly questions One or more of these:
... and if required: "What" symbol card |
Responds to who questions
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Familiar picture books
|
| Teach these concepts using repeated phrases and matching them as much as possible with the relevant symbol. Allow thinking time. Reward any attempts. |
| Photos of people One or more of these:
...and if required:
| You may need to give the child a language model before he/she can ask a 'who' question. | |
| Who is around? A situation where there are other people - for example in class, in the playground. "Who" symbol card if required. |
Support Commtap to keep it online
Thank you for visiting Commtap.
Please read this message as it is extremely important.
- Visitor donations mean we can continue to host over 1,000 free activities to support speech, language, and communication development.
- Visitor donations mean we can continue to provide free resources to address a wide range of communication needs, including limited speech or language, interaction challenges, and needs associated with conditions such as developmental language disorder, autism, and cerebral palsy.
- Visitor donations mean we can continue to provide resources to support the work of speech and language therapists, teachers, teaching assistants, parents, and carers.
- Visitor donations mean we can continue to provide the free key word sign dictionary (bks.org.uk) which has over 2,000 Makaton and Signalong signs.
We know that not everyone is able to afford to pay to access these resources, however, if you can, please make a donation to keep the site going.
Thank you
Google ads on this page are provided by Google Adsense - and their presence does not imply any endorsement by Commtap. Report a problem with an ad on this page. Log in (for free) to avoid seeing Google ads.