Search
User login
Topic “Small group”
Contains activities or strategies suitable for a small group.
Understanding and hearing the difference between noisy (voiced) and quiet (voiceless) sounds
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Understanding the concepts of noisy/quiet | 1. Before working on the activities below, make sure your child has an understand of the concepts of noisy/quiet. Click on link under materials section for activities relating to these concepts.
| |
| Noisy/Quiet Speech Sounds - printable noisy/quiet symbols - sound picture cards - you may have a set of phonic cards given to you by your speech and language therapist or education setting (e.g. Jolly Phonics, Nuffield Dyspraxia Resources) - Use these resources if you have them. If you do not have a set of phonic resources you can use click here to for a printable resource. - optional - you could use noisy/quiet characters from Mr Men books by Roger Hargreaves. | Once your child is able to recgonise the differene between noisy and quiet sounds you can move on to: 1. Listening to the difference between sounds in words 2. To add link - production of sounds | |
|
|
Identifying and saying the correct sound blend at the beginning of words
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Stick it - A piece of paper for each of the blend sounds you are working on, e.g. for 's' blends you would have 'sc/sk' 'sl' 'sm' 'sn' 'sp' 'st' 'sw' - Glue/Blu-tac - Pen/pencil - Feely-bag/ other container - A selection of picture cards with words starting with your target blends/clusters - this will either be 's' blends, 'l' blends or 'r' blends - click here for printable picture cards. | 1. Help the child to write a different sound blend in the centre of each sheet of paper. 2. Put all the pictures in the feely-bag or container. Shake it to mix them up. 3. Ask the child to pull one picture out of the feely-bag. 4. Ask them to say the name of the picture. Give them a clue if they are not sure what the picture shows. Model the correct pronunciation if the child says it wrong. 5. Ask the child to stick the picture on the correct piece of paper according to the blend at the start of the word. (Use Blu-tac if you want to be able to re-use the pictures). 6. Repeat until all the pictures have been used up. | If the child finds it hard to hear the cluster at the start of the word when they say it themselves, you could say it to them. If they still find it hard, say the word with a short break after the cluster, e.g. "sk...irt". If the child mispronounces the word say the word both correctly and the way the child says it, and ask them which is the correct one e.g. "is it 'stooter' or 'scooter'?" |
use adjectives to describe and classify objects
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Classify the object 1
| 1. Decide on a common category e.g. "things which are round" or "things which are red". 2. Help the child to sort the items into 2 groups according to whether they fit the category or not (i.e. a 'red' group and a 'not red' group). | |
| Classify the object 2 A selection of common objects (you could use pictures instead) 2 sorting rings (draw two overlapping circles on a large sheet of paper if these are not available)
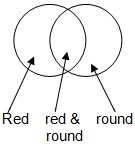
Category labels (optional) | 1. Decide on two common categories e.g. "things which are round" and "things which are red". 2. Place the sorting rings on the table so that they overlap. 3. Explain that one ring is for items that have one feature (e.g. "round"). Explain that the other ring is for items that have the other feature (e.g. "red"). Explain that where the rings overlap, is where things that have both features go (see diagram on the left). Items which do not fit either category are left outside the rings. 4. Add labels if you are using them. 5. Help the child to sort the items into groups according to which category they fit. | To make this activity more difficult, you could sort according to three categories. |
| Spider chart
| Example of a spider chart:
| |
| What's in the bag?
| ||
| Nicknames No materials required | Works well as a group activity - could be used as an ice-breaker. | |
| I spy adjectives No materials required. | ||
| Books
|
sort items by property and function
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Categories Challenge Picture cards. These can be related to class topic vocabulary | Have each adult and child in the group take it in turns to make the cards into 2 groups (or 3 if necessary). The cards in each group must all share a property or a function e.g. made of metal / transport (encourage the children not to base their groups purely on appearance). Write down the categories that are thought of, so that the children can review them. | This is a very flexible activity, which can be used for a very wide range of vocabulary. If the children can read, you could use written words rather than pictures. |
| Shopping List Flash cards with possible properties and functions written on them (e.g. hard, rough, things you wear, things you use to cut with, things you can read, etc.) A dice | If 6 items is too challenging, use a 1 - 3 dice. You could also extend the activity by having the other children in the group add more items to a group. You could stick the flash card into a notebook, and write / draw each item that is thought of around it. Each time you do the activity you will be building up a bank of words linked into categories. | |
| Add One Assorted picture cards. (They can be linked to class topic vocabulary. Make sure there are cards from a range of different categories) | This activity should only be used with vocabulary items the children are familiar with. When the children have a number of cards, it will be easier if they can make more than 3 groups. If they are finding it challenging, remove the time pressure. This means that each child has as long as they need to make 2 or 3 groups. When each child has finished, everyone then takes an additional card. | |
| Semantic Links This activity requires the purchasing of a commercial programme. SLTs/specialist teachers - help to further develop this sheet by providing an example or description of alternative resources to use in this activity. Worksheet from Semantic Links programme - available from Stass Publications Choose one with 3 choices. |
sort materials by properties and function
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Object properties race track game Pictures of everyday objects from classroom or home, or real objects. Cards with words and symbols of actions e.g. cut, stretch, squash Dice Counters You can create cards with symbols for actions using the Commtap Symboliser for PowerPoint. | Explain that you are going to be thinking about things you see around you, and what you can do to them. Discuss each of the action cards, and model each action. E.g. stretch - stretch a rubber band Lay the picture cards out in a simple race track. Put the action cards up where you can all see them. Take turns to throw a dice and move round the track. Turn over the picture card you land on and say which one of the actions can be done to that object. The first person to the end of the track wins. | It is important to check the child understands the actions, and knows what the objects are. |
| Object properties card sorting game Cards with words and symbols of actions Bag / box Pictures of objects from school, or home / real objects Sandtimer You can create cards with symbols for actions using the Commtap Symboliser for PowerPoint. | It is important to check the child understands the actions, and knows what the objects are. | |
| Actions with everyday objects Pictures of everyday objects from classroom or home, or real objects. Cards with words and symbols of activities e.g. eat, draw You can create cards with symbols for actions using the Commtap Symboliser for PowerPoint. | ||
| Object properties four in a row game Pictures of everyday objects from classroom or home, or real objects. Cards with words and symbols of activities e.g. eat, draw Counters in 2 colours - 10 each. You can create cards with symbols for actions using the Commtap Symboliser for PowerPoint.
| To make this easier, put cards up where you can see them showing a range of activities to choose from. |
understand why questions in context and respond
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| The Disastrous Day A Playmobil figure or similar Small world objects - some of them broken | 1. Explain that you are going to tell a story about the toy. 2. Tell a story about what the toy does in the day. Lots of things go wrong because the objects are broken e.g. 'want to go to work in the car but it won't move.' 3. Whenever there is a problem for the toy, ask the child 'why?' e.g. 'why won't the car move?' Answer: 'because there is no wheel!' | Give the child a turn at telling the story too. |
| Freddy's Travels A toy character (called Freddy) Pictures of different locations, e.g. beach, mountains One or two items which go with each location e.g. bucket and swimming costume for the beach | ||
| Animal Adventure Pictures of different locations with different 'hazards' or things of interest e.g. a jungle with a river and dinosaurs Two toy animals (wind up toys are ideal) | Use your imagination! | |
| Problem solving Equipment to demonstrate an everyday problem and discuss it. Some examples of equipment you could use: Torch or toy with no batteries; Cup with a hole in it; Dry pasta; Pen with no nib and in; Broken pencil; Dry pen with no lid. | You will need to think of a problem in advance - see the list in the materials column. This activity is ideal to do throughout the child's day, whenever there is a problem to be solved! |
Identify errors in pictures of everyday objects
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| What is wrong? pictures Pictures of everyday objects and situations with errors, for example a picture of a house with the front door on the second floor, a picture of a phone with a banana instead of a handset, a someone using an umbrella with holes in it in the rain Commercially produced "What's Wrong?" cards are available. If you have any of your own pictures appropriate for this activity or you know of a link, please consider adding them to the site at www.commtap.org | 1. Have a look at the card and get the child to identify what is wrong or unusual about what is depicted on the card. 2. Get the child to talk about what problems could arise from the situation in the picture and how they could be resolved. 3. Get the child to relate the picture to their own experience. | If the child has difficulties, you can look surprised or puzzled when you see the picture, make comments like "there's something wrong", or "my phone's not like that", or "Oh no! He's getting wet!" To keep the child motivated they could also post the card once the card has been discussed. |
matches related everyday objects
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Find and match Pairs of related objects, for example: pencil and paper sock and a shoe bar of soap and a flannel, toothbrush and a tube of toothpaste hammer and nail knife and fork box | 1. Select pairs of related objects; 2. Place one member of each of the object pairs in front of the child (e.g. pencil, sock, soap, toothbrush); 3. Place the remaining objects (e.g. paper, shoe, flannel, toothpaste) in a box; 4. Have the child pick an object from the box and ask them to "Find the one we use with this"; 5. Repeat with the rest of the objects in the box. | If necessary, demonstrate how the objects go together, or get the child to show you. If the child chooses the wrong item, you can look puzzled and try and use those items together. For example try and write on the paper with a toothbrush. Then you can try and find the right item, and look pleased with yourself/ express happiness when you find you can make marks on the paper. |
removes object from face that obscures vision
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Cloth and Peek-a-boo Place cloth over Child's face | Place cloth on Child's face, wait and see if he makes any reaction, then pull it off saying 'peek-a-boo' | Child will need time to become familiar with the routine of the activity Use simple words like 'gone' and 'hello' |
| Cloth and Song 'Where is Child? Where is Child? Here he is! Here he is!' To the tune of 'Frere Jaques' | Child will need time to become familiar with the routine of the activity |
puts and takes objects into and out of container
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Box and Bricks Box Bricks | Empty the bricks on the floor or table Help child pick up a brick and place it in the box... Remember to use simple words like 'in', 'more'... When all the bricks are in the box say 'all in, no more!' (or something similar!) Then help child take them out again - say 'out', 'more' etc | Initially he might need to be helped (hand-over-hand) to pick up brick, place hand in/near box and prompted to drop it The aim to develop child's ability to do this more and more independently... |
| Post Box Commercial or home made post box, pictures or objects to post | Remember to use simple words and comment on what is happening... | |
| Monkey Eating Monkey box and plastic food | Remember to use simple names ( 'apple') and 'in' and noises like 'mmm', 'yum yum' etc |
To knock down a tower deliberately
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Tower Building - 4-5 bricks or other items that will stack. | - Show your child the items. - Stack them on top of each other - use words while you are stacking, this could be the number, e.g. 1, 2, 3..., or the colour, e.g. red, green yellow, or brick, more bricks. - Use 'ready steady...' or 'i, 2, 3 knock down' while you knock the tower down. - Rebuild the tower and carry out the sequence again. - When your child becomes familiar with this routine see if they copy you by knocking the tower down. |
identify and discuss errors made by others
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| What's wrong pictures What's wrong pictures (e.g. LDA, Colorcards) Pen and paper | 1. Choose a picture (or let the child choose one). Both people look at it. Take it in turns to describe the picture and say how it should look. Make sure you have a new picture to describe each time. 2. Take it in turns to choose a picture, which you keep hidden from the other person. Describe the picture while the other person tries to draw it based on your description. Compare the drawing to the original picture and say how the picture should look. If the drawing does not look very much like the picture, say why this went wrong. | |
| Did I get it right? Large composite pictures (e.g. "passages a decouvrir"). Score sheet (2 columns - one with your name at the top, the other with the child's) Pen | Some children find it extremely difficult to correct adults, even if the adult's mistake means the child gets something wrong (for example colouring a banana blue because the adult passed the wrong pen). You may need to reassure the child that it's ok to correct you. |
Turn taking 2
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Marble run game Marble run game; Waiting cards. |
| Keep this activity for the end of a small group work session. Keep the activity short and snappy so that the children keep motivated. Choose really interesting toys for this activity that the children don't have general access to. |
| Songs Box of song cards with a name/picture for each song that could be chosen. |
| Keep the song short - only sing a bit of it to avoid the children having to wait to long between choosing a song. |
| A bag with a selection of appealing toys inside | ||
| Stickers Variety of stickers - for example of cartoon characters, cars, animals etc. | You could do this activity as an activity to end a group session. Some children may find it difficult to peel off a sticker - give them minimum help to do it themselves, for example peeling up a small corner of a sticker. | |
| Bubbles Pot of bubbles liquid. | Depending on the children, it may be easier (and less messy!) to pass the bubble wand (stick) around and for you to keep hold of the bubbles container - on their turn they dip the wand into the bubbles to blow. | |
| Musical instruments One drum or other instrument. Or, on drum or other instrument for each child. | ||
| Any other high interest activity game that can be used in a small group Game Waiting cards |
Turn taking 1
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Play a game with adult supervision Marble run; Bricks for sharing building and knocking down a tower; Any lotto game where pictures have to be matched; Skittles; Pushing cars down a run/pipe. |
| Keep turns short and snappy so children don't need to wait too long. Keep the time spent on the whole game short and snappy so children don't get bored. Support good waiting by saying "you are waiting..." sometimes the child will find it easier to wait if they have something to hold while they wait. You might need to make a chart of your child's name and the friend's name and point to each name at the appropriate time to make the idea of turn taking more visible. |
respond appropriately with no to short phrases
| Activity/strategy name and materials required | How to do the activity | Key principles for doing the activity and comments |
|---|---|---|
| Items from a bag 1 Bag Set of objects which the child understands the names of | 1. Take the objects out of the bag one at a time, for each item say to the child "It's a [name of object]" for example "It's an apple". Look to the child for confirmation that it's an apple (as if you are not quite sure). Then, with certainty, say "Yes, it's an apple"; 2. After a few items, start to get the occasional item wrong (use exactly the same not-quite-sure facial expression you used before). E.g. "It's a pencil" (but it's a toy car). Can the child tell you that it isn't? If not, have a look at the item again and pretend to suddenly realise you were wrong, say "(oh) No, it's not a pencil. It's a car. 3. Repeat. | This activity requires a bit of play acting to work well. Over time you may be able to name/incorrectly name items more quickly, and be more positive about being right every time (even though you are not). |
| Jemima and Polly Two toy animals or dolls (each with a name) (Optional) things that the dolls can use, e.g. tea set |
Support Commtap to keep it online
Thank you for visiting Commtap.
Please read this message as it is extremely important.
- Visitor donations mean we can continue to host over 1,000 free activities to support speech, language, and communication development.
- Visitor donations mean we can continue to provide free resources to address a wide range of communication needs, including limited speech or language, interaction challenges, and needs associated with conditions such as developmental language disorder, autism, and cerebral palsy.
- Visitor donations mean we can continue to provide resources to support the work of speech and language therapists, teachers, teaching assistants, parents, and carers.
- Visitor donations mean we can continue to provide the free key word sign dictionary (bks.org.uk) which has over 2,000 Makaton and Signalong signs.
We know that not everyone is able to afford to pay to access these resources, however, if you can, please make a donation to keep the site going.
Thank you
Google ads on this page are provided by Google Adsense - and their presence does not imply any endorsement by Commtap. Report a problem with an ad on this page. Log in (for free) to avoid seeing Google ads.